Przejdź do trybu offline z Player FM !
How Memory Works: A Guide Anyone Can Understand
Archiwalne serie ("Kanał nieaktywny" status)
When?
This feed was archived on February 19, 2024 00:56 (
Why? Kanał nieaktywny status. Nasze serwery nie otrzymały odpowiedzi od kanału przez zbyt długi czas.
What now? You might be able to find a more up-to-date version using the search function. This series will no longer be checked for updates. If you believe this to be in error, please check if the publisher's feed link below is valid and contact support to request the feed be restored or if you have any other concerns about this.
Manage episode 317524520 series 1375140
 Memory works like breathing and blinking. Here’s why:
Memory works like breathing and blinking. Here’s why:
You can control your brain function to a certain extent and it operates entirely on autopilot, whether you’re paying attention to it or not.
How do we know?
Think about your home.
Did you have to work hard to learn the layout?
Probably not. You probably learned it automatically.
The alphabet, on the other hand, required exercises and repetition over weeks. Your teachers guided the process.
As an adult, you need to guide the memory process yourself when you want to learn new information.
Given that memory is both an automatic process and a tool we can use deliberately, how exactly does it work?
The answer is fascinating and comes with many clues that will help you improve it.
Let’s dig in.
How Does Human Memory Work? The 3 Main Processes
Scientists think that memory is built from processes that work together. These processes involve multiple neural pathways and include:
- Encoding
- Storing
- Retrieving, or decoding
Encoding
Encoding takes place during and after information enters your brain through the senses. It starts with the initial impression and interpretation of information.
Take the example of learning your home layout. In Human Spatial Memory: Remembering Where, the authors present a number of theories of how encoding begins and produces a memory trace that leads to consolidation.
One of their theories suggests that our brains remember spatial layouts by determining which objects are on top of other objects.
In other words, you remember the location of the kitchen because the countertops and the stop stand on top of its floor. The tub is on top of the bathroom floor, etc. The brain then uses what is called its “coordinate system” to encode the information.

One theory of memory says that our brains track surfaces and what objects or on top of other objects in order to remember our environments.
When it comes to learning information like a language, we can deeply integrate with the process by using one of several forms of active recall.
How are Memories Stored In The Brain?
In terms of storage, scientists think our spatial information may reside in the parietal lobe. They’ve reached this conclusion because damage to this area of the brain disturbs our spatial awareness. The hippocampus also plays a key role, specifically in consolidation and transferring information from short-term to long-term storage.
Storage is a big topic because it’s not clear that information ever really stays put in the brain.
On the contrary, scientists have shown that information we’ve memorized moves around over time. Memory expert Dr. Gary Small likens this movement to how families travel from homes around the world to gather in one specific building for Thanksgiving dinner once a year.
Retrieval (Decoding)
Dr. Small’s analogy suggests that our memories are actually split apart and keep moving around in the brain. Then, when we retrieve the memories, they move to a single location so we can perceive them as something that feels whole.
And when our recall does not feel whole and complete, that’s because some parts of the memories did not make it to the party.
Here’s more detail on recall and retrieval with more details on where memories are stored.
How Are Memories Formed?
People tend to think that long term memories take time to form.
However, scientists know this not to be the case. Not only can certain protein synthesis formations rapidly form long term memories, we also experience flashbulb memory.
Either way, the direct answer to how memories form is neurochemical. It is literally the collaboration of existing brain structures working together to “connect” in order to facilitate retention and recollection of multiple details.
You can even see the process take place with your own eyes as neurons and synapses find one another and connect:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m0rHZ_RDdyQ
As memories connect, myelin wraps around the connections. The strength of any given memory appears related to the robustness of the connection itself, the strength of the myelin sheath and the length of the dendritic spines on the neurons.
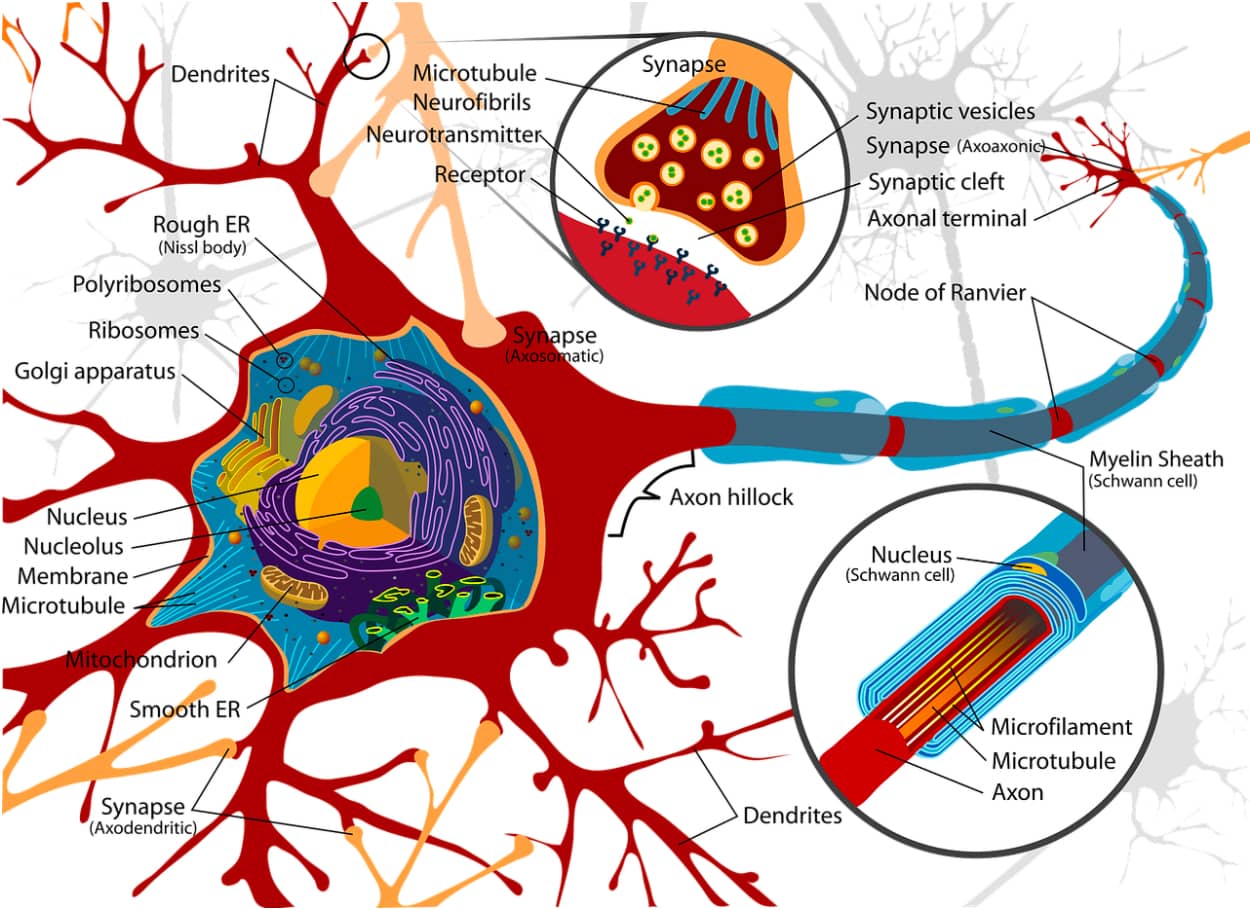
Although the exact process of how memories are formed and stored is still not well-understood, scientist and memory expert David Eagleman claims in The Brain that every healthy brain has room for a zettabyte of information.
Where Are Memories Stored?
As mentioned, the brain stores memory throughout its structures. And the exact location of individual memories can and does change.
This means that the most direct answer to the question is that our memories are stored in our synapses. They are literally stored in connections.
But there’s another way to think about the question.
Memories aren’t just stored in your brain.
They are stored in the brains of other people.
In books.
Movies.
Recorded music.
Library archives.
Our species has devised alphabets, words and grammars to help us encode knowledge in a variety of mediums. To focus only on the brain is missing the point.
But what remains the same is the focus on our memories being stored in the connections themselves.
As you read this post, you are connecting your brain to mine. My remembered knowledge about memory is flowing into your brain. And if you decide to engage with it deeply, this knowledge will become part of your knowledge-set.
If you don’t, the fact of your individual forgetting does not mean the information isn’t stored somewhere. It will still be right here on this page, located in the memory of multiple computers across the Internet.

We tend to think that memory is stored in our minds. In reality, it is stored in multiple locations and devices, if not in the connections between things themselves.
My suggestion is an example of abstract thinking about memory, and I’m confident that when you reflect on the point, you’ll agree that it’s true.
Ultimately, I think the most interesting type of memory involves new research. It suggests that synapses do not store memories at all. Rather, DNA and RNA store our memories.
This new and emerging research is worth keeping an eye on. The animal testing will likely reproduce in future human trials.
The Main Types of Memory
Confused by all the types of memory you find people talking about?
I don’t blame you. There are a ton of them.
Luckily, we can break them down into the three main types of memory. Then there are all the rest.
The biggest three are:
- Sensory memory
- Short-term memory
- Long term memory
After that, memory scientists break the categories down into:
- Episodic memory
- Autobiographical memory
- Procedural memory
- Working memory
- Semantic memory
- Iconic memory
- Visual memory
- Context-dependent memory
- Prospective memory
- Echoic memory
- Implicit memory
- Non-declarative memory
- Explicit memory
- Eidetic memory
In addition, you’ll find special topics like:
- Focused attention
- Crystal and fluid intelligence
- Synesthesia
- Hyperphantasia
- Serotonin and memory
- Amnesia
- Long term memory loss
- Stress and memory loss
- Memory disorders
- The myth of photographic memory
Conclusion: How to Improve Your Memory
Luckily, you can easily improve your memory.
The first step is to pay attention as much as possible.
Then, you’ll want to learn various techniques. The most important are:
- The Memory Palace technique
- The Major Method
- The Pegword Method
- PAO System
To place the foundations of these memory improvement skills in your hands, grab this FREE Memory Improvement Kit:
The best part?
Once you have superior memory skills, it’s easy to remember all the different kinds of memory we discussed today.
It’s a real win-win for you and the world. The more we understand about how memory functions and what exactly it is, the more people can better navigate reality and lead more fulfilling lives.
So what do you say? Are you ready to live a life more connected to the information storage and retrieval device alive and well in your head?
488 odcinków
Archiwalne serie ("Kanał nieaktywny" status)
When?
This feed was archived on February 19, 2024 00:56 (
Why? Kanał nieaktywny status. Nasze serwery nie otrzymały odpowiedzi od kanału przez zbyt długi czas.
What now? You might be able to find a more up-to-date version using the search function. This series will no longer be checked for updates. If you believe this to be in error, please check if the publisher's feed link below is valid and contact support to request the feed be restored or if you have any other concerns about this.
Manage episode 317524520 series 1375140
 Memory works like breathing and blinking. Here’s why:
Memory works like breathing and blinking. Here’s why:
You can control your brain function to a certain extent and it operates entirely on autopilot, whether you’re paying attention to it or not.
How do we know?
Think about your home.
Did you have to work hard to learn the layout?
Probably not. You probably learned it automatically.
The alphabet, on the other hand, required exercises and repetition over weeks. Your teachers guided the process.
As an adult, you need to guide the memory process yourself when you want to learn new information.
Given that memory is both an automatic process and a tool we can use deliberately, how exactly does it work?
The answer is fascinating and comes with many clues that will help you improve it.
Let’s dig in.
How Does Human Memory Work? The 3 Main Processes
Scientists think that memory is built from processes that work together. These processes involve multiple neural pathways and include:
- Encoding
- Storing
- Retrieving, or decoding
Encoding
Encoding takes place during and after information enters your brain through the senses. It starts with the initial impression and interpretation of information.
Take the example of learning your home layout. In Human Spatial Memory: Remembering Where, the authors present a number of theories of how encoding begins and produces a memory trace that leads to consolidation.
One of their theories suggests that our brains remember spatial layouts by determining which objects are on top of other objects.
In other words, you remember the location of the kitchen because the countertops and the stop stand on top of its floor. The tub is on top of the bathroom floor, etc. The brain then uses what is called its “coordinate system” to encode the information.

One theory of memory says that our brains track surfaces and what objects or on top of other objects in order to remember our environments.
When it comes to learning information like a language, we can deeply integrate with the process by using one of several forms of active recall.
How are Memories Stored In The Brain?
In terms of storage, scientists think our spatial information may reside in the parietal lobe. They’ve reached this conclusion because damage to this area of the brain disturbs our spatial awareness. The hippocampus also plays a key role, specifically in consolidation and transferring information from short-term to long-term storage.
Storage is a big topic because it’s not clear that information ever really stays put in the brain.
On the contrary, scientists have shown that information we’ve memorized moves around over time. Memory expert Dr. Gary Small likens this movement to how families travel from homes around the world to gather in one specific building for Thanksgiving dinner once a year.
Retrieval (Decoding)
Dr. Small’s analogy suggests that our memories are actually split apart and keep moving around in the brain. Then, when we retrieve the memories, they move to a single location so we can perceive them as something that feels whole.
And when our recall does not feel whole and complete, that’s because some parts of the memories did not make it to the party.
Here’s more detail on recall and retrieval with more details on where memories are stored.
How Are Memories Formed?
People tend to think that long term memories take time to form.
However, scientists know this not to be the case. Not only can certain protein synthesis formations rapidly form long term memories, we also experience flashbulb memory.
Either way, the direct answer to how memories form is neurochemical. It is literally the collaboration of existing brain structures working together to “connect” in order to facilitate retention and recollection of multiple details.
You can even see the process take place with your own eyes as neurons and synapses find one another and connect:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m0rHZ_RDdyQ
As memories connect, myelin wraps around the connections. The strength of any given memory appears related to the robustness of the connection itself, the strength of the myelin sheath and the length of the dendritic spines on the neurons.

Although the exact process of how memories are formed and stored is still not well-understood, scientist and memory expert David Eagleman claims in The Brain that every healthy brain has room for a zettabyte of information.
Where Are Memories Stored?
As mentioned, the brain stores memory throughout its structures. And the exact location of individual memories can and does change.
This means that the most direct answer to the question is that our memories are stored in our synapses. They are literally stored in connections.
But there’s another way to think about the question.
Memories aren’t just stored in your brain.
They are stored in the brains of other people.
In books.
Movies.
Recorded music.
Library archives.
Our species has devised alphabets, words and grammars to help us encode knowledge in a variety of mediums. To focus only on the brain is missing the point.
But what remains the same is the focus on our memories being stored in the connections themselves.
As you read this post, you are connecting your brain to mine. My remembered knowledge about memory is flowing into your brain. And if you decide to engage with it deeply, this knowledge will become part of your knowledge-set.
If you don’t, the fact of your individual forgetting does not mean the information isn’t stored somewhere. It will still be right here on this page, located in the memory of multiple computers across the Internet.

We tend to think that memory is stored in our minds. In reality, it is stored in multiple locations and devices, if not in the connections between things themselves.
My suggestion is an example of abstract thinking about memory, and I’m confident that when you reflect on the point, you’ll agree that it’s true.
Ultimately, I think the most interesting type of memory involves new research. It suggests that synapses do not store memories at all. Rather, DNA and RNA store our memories.
This new and emerging research is worth keeping an eye on. The animal testing will likely reproduce in future human trials.
The Main Types of Memory
Confused by all the types of memory you find people talking about?
I don’t blame you. There are a ton of them.
Luckily, we can break them down into the three main types of memory. Then there are all the rest.
The biggest three are:
- Sensory memory
- Short-term memory
- Long term memory
After that, memory scientists break the categories down into:
- Episodic memory
- Autobiographical memory
- Procedural memory
- Working memory
- Semantic memory
- Iconic memory
- Visual memory
- Context-dependent memory
- Prospective memory
- Echoic memory
- Implicit memory
- Non-declarative memory
- Explicit memory
- Eidetic memory
In addition, you’ll find special topics like:
- Focused attention
- Crystal and fluid intelligence
- Synesthesia
- Hyperphantasia
- Serotonin and memory
- Amnesia
- Long term memory loss
- Stress and memory loss
- Memory disorders
- The myth of photographic memory
Conclusion: How to Improve Your Memory
Luckily, you can easily improve your memory.
The first step is to pay attention as much as possible.
Then, you’ll want to learn various techniques. The most important are:
- The Memory Palace technique
- The Major Method
- The Pegword Method
- PAO System
To place the foundations of these memory improvement skills in your hands, grab this FREE Memory Improvement Kit:
The best part?
Once you have superior memory skills, it’s easy to remember all the different kinds of memory we discussed today.
It’s a real win-win for you and the world. The more we understand about how memory functions and what exactly it is, the more people can better navigate reality and lead more fulfilling lives.
So what do you say? Are you ready to live a life more connected to the information storage and retrieval device alive and well in your head?
488 odcinków
Wszystkie odcinki
×Zapraszamy w Player FM
Odtwarzacz FM skanuje sieć w poszukiwaniu wysokiej jakości podcastów, abyś mógł się nią cieszyć już teraz. To najlepsza aplikacja do podcastów, działająca na Androidzie, iPhonie i Internecie. Zarejestruj się, aby zsynchronizować subskrypcje na różnych urządzeniach.





