Przejdź do trybu offline z Player FM !
Encore: What Is Appalachia? We Asked People From Around The Region. Here’s What They Said
Manage episode 459202703 series 2471658
This week, we’re revisiting our episode “What Is Appalachia?” from December 2021. Appalachia connects mountainous parts of the South, the Midwest, the Rust belt and even the Northeast. The Appalachian Regional Commission defined the boundaries for Appalachia in 1965 with the creation of the Appalachian Regional Commission, a part of Lyndon B. Johnson’s War on Poverty. It was legislation that sought to expand social welfare, and some localities were eager for the money, while others resisted the designation. The boundaries and definition of Appalachia can now only be changed by an act of Congress.
Politically, Appalachia encompasses 423 counties across 13 states — and West Virginia’s the only state entirely inside the region.
That leaves so much room for geographic and cultural variation, as well as many different views on what Appalachia really is.
For Inside Appalachia, we turned our entire episode over to the question, “What is Appalachia?” With stories from Mississippi to Pittsburgh, we asked people across our region whether they consider themselves to be Appalachian.
Mississippi
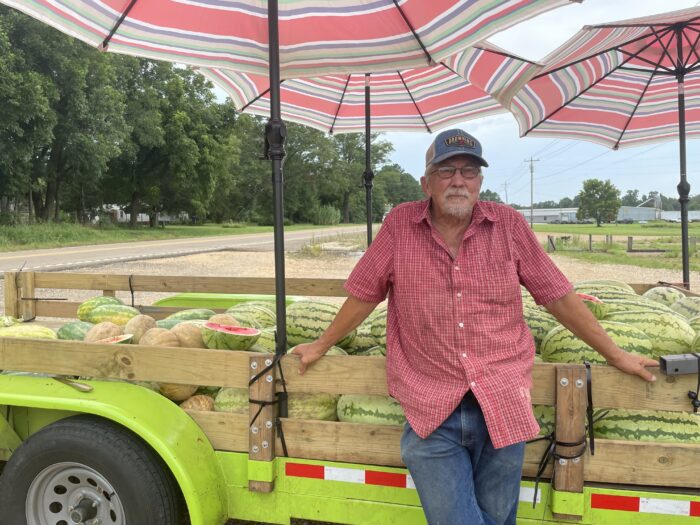

Credit: Caitlin Tan/West Virginia Public Broadcasting
Bob Owens is a watermelon farmer outside New Houlka, in the northeastern part of Mississippi. Owens said he was aware that Mississippi is part of Appalachia, but that no one in the state would consider themselves Appalachian. “I consider myself the worst redneck you’ve ever seen,” Owens said. “I live in the area of the Appalachian mountain range — not part of it, but close to it. So I guess you call me a redneck Appalachian.” This is the general consensus among the people in Mississippi we spoke to.
Geographically, the foothills of the Appalachian mountain range are located in northern Mississippi. The state’s tallest point is Woodall Mountain, 806 feet in elevation. For reference, the highest point in North Carolina, Mount Mitchell, is more than 6,600 feet in elevation, eight times higher than Woodall Mountain.
Co-host Caitlin Tan spoke with Texas State University History professor Justin Randolph, who wrote an essay for “Southern Cultures” called “The Making of Appalachian Mississippi.” Randolph argues in his essay that Mississippi became part of Appalachia for political and racial reasons, as well as economic advantages the designation brought to the 24 counties in Mississippi that were included in the ARC’s boundaries.
Shenandoah Valley
In the 1960s, while some localities were clamoring to get into Appalachia, on the eastern edge of the region, some lawmakers fought to keep their counties outside the boundaries, including politicians in Roanoke, Virginia and the Shenandoah Valley. Appalachian Studies associate professor Emily Satterwhite said explaining to her students why some counties in Virginia are included in Appalachia, but others aren’t, is confusing. “
The students in front of me are wondering why they're not included,” White said.
Pittsburgh
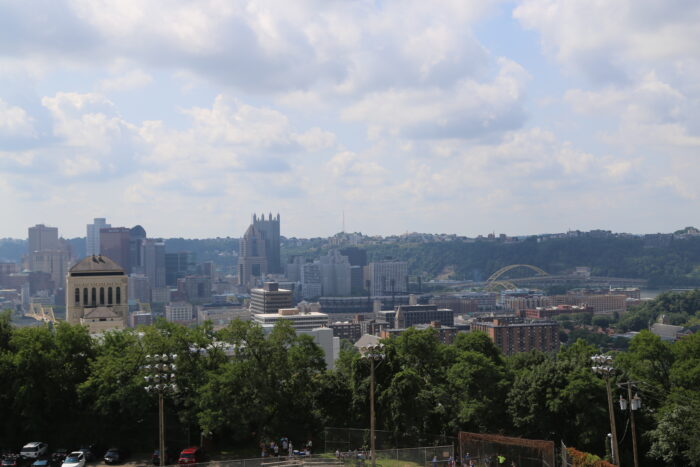

Courtesy
Appalachia’s largest city is Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. When we asked people from that city to tell us if they consider it a part of Appalachia, about half said no. “I definitely do not feel that I am Appalachian culturally,” said Mark Jovanovich, who grew up just outside Pittsburgh’s city limits in the Woodland Hills area. “Personally, I would consider the city of Pittsburgh is sort of like a mini New York City. I guess we'd probably be lumped in as like a Rust Belt city, which makes enough sense, but definitely not Appalachian culturally.”
Writer Brian O’Neill disagrees. He wrote a book called The Paris of Appalachia: Pittsburgh in the Twenty-First Century. “My original title for the book was ‘I love Pittsburgh like a brother and my brother drives me nuts.’”
An editor advised him to change the title of his book to a phrase that he said is sometimes used to refer to Pittsburgh derisively. “I couldn't figure out why that should be a putdown, because Paris is nice. And Appalachia is a beautiful part of the world. And if we were called the Paris of the Rockies, we wouldn't run from that. So why would we run from this? Why don't we embrace it? So that became the title of my book.”
He said that geographically, Pittsburgh is clearly in the Appalachian Mountains. “I mean, this is one mountain range that stretches from Georgia to Maine. And the idea that it belongs only to the southern part of the mountain range defies logic to me,” O’Neill said.
What Do You Think?
How about you? Do you call yourself an Appalachian? Why or why not? Send us an email to InsideAppalachia@wvpublic.org.
------
Our theme music is by Matt Jackfert. Other music this week was provided by John Wyatt, John R Miller, Alan Cathead Johnston, and Dinosaur Burps. Roxy Todd originally produced this episode. Bill Lynch is our current producer. Our executive producer is Eric Douglas. Alex Runyon was our associate producer on this original episode. Kelley Libby is our editor. Our audio mixer is Patrick Stephens. Zander Aloi also helped produce this episode.
You can find us on Instagram, Threads and Twitter @InAppalachia. Or here on Facebook.
Inside Appalachia is a production of West Virginia Public Broadcasting.

107 odcinków
Encore: What Is Appalachia? We Asked People From Around The Region. Here’s What They Said
Podcast - Inside Appalachia Story Archives - West Virginia Public Broadcasting
Manage episode 459202703 series 2471658
This week, we’re revisiting our episode “What Is Appalachia?” from December 2021. Appalachia connects mountainous parts of the South, the Midwest, the Rust belt and even the Northeast. The Appalachian Regional Commission defined the boundaries for Appalachia in 1965 with the creation of the Appalachian Regional Commission, a part of Lyndon B. Johnson’s War on Poverty. It was legislation that sought to expand social welfare, and some localities were eager for the money, while others resisted the designation. The boundaries and definition of Appalachia can now only be changed by an act of Congress.
Politically, Appalachia encompasses 423 counties across 13 states — and West Virginia’s the only state entirely inside the region.
That leaves so much room for geographic and cultural variation, as well as many different views on what Appalachia really is.
For Inside Appalachia, we turned our entire episode over to the question, “What is Appalachia?” With stories from Mississippi to Pittsburgh, we asked people across our region whether they consider themselves to be Appalachian.

Mississippi

Credit: Caitlin Tan/West Virginia Public Broadcasting
Bob Owens is a watermelon farmer outside New Houlka, in the northeastern part of Mississippi. Owens said he was aware that Mississippi is part of Appalachia, but that no one in the state would consider themselves Appalachian. “I consider myself the worst redneck you’ve ever seen,” Owens said. “I live in the area of the Appalachian mountain range — not part of it, but close to it. So I guess you call me a redneck Appalachian.” This is the general consensus among the people in Mississippi we spoke to.
Geographically, the foothills of the Appalachian mountain range are located in northern Mississippi. The state’s tallest point is Woodall Mountain, 806 feet in elevation. For reference, the highest point in North Carolina, Mount Mitchell, is more than 6,600 feet in elevation, eight times higher than Woodall Mountain.
Co-host Caitlin Tan spoke with Texas State University History professor Justin Randolph, who wrote an essay for “Southern Cultures” called “The Making of Appalachian Mississippi.” Randolph argues in his essay that Mississippi became part of Appalachia for political and racial reasons, as well as economic advantages the designation brought to the 24 counties in Mississippi that were included in the ARC’s boundaries.
Shenandoah Valley
In the 1960s, while some localities were clamoring to get into Appalachia, on the eastern edge of the region, some lawmakers fought to keep their counties outside the boundaries, including politicians in Roanoke, Virginia and the Shenandoah Valley. Appalachian Studies associate professor Emily Satterwhite said explaining to her students why some counties in Virginia are included in Appalachia, but others aren’t, is confusing. “
The students in front of me are wondering why they're not included,” White said.
Pittsburgh

Courtesy
Appalachia’s largest city is Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. When we asked people from that city to tell us if they consider it a part of Appalachia, about half said no. “I definitely do not feel that I am Appalachian culturally,” said Mark Jovanovich, who grew up just outside Pittsburgh’s city limits in the Woodland Hills area. “Personally, I would consider the city of Pittsburgh is sort of like a mini New York City. I guess we'd probably be lumped in as like a Rust Belt city, which makes enough sense, but definitely not Appalachian culturally.”
Writer Brian O’Neill disagrees. He wrote a book called The Paris of Appalachia: Pittsburgh in the Twenty-First Century. “My original title for the book was ‘I love Pittsburgh like a brother and my brother drives me nuts.’”
An editor advised him to change the title of his book to a phrase that he said is sometimes used to refer to Pittsburgh derisively. “I couldn't figure out why that should be a putdown, because Paris is nice. And Appalachia is a beautiful part of the world. And if we were called the Paris of the Rockies, we wouldn't run from that. So why would we run from this? Why don't we embrace it? So that became the title of my book.”
He said that geographically, Pittsburgh is clearly in the Appalachian Mountains. “I mean, this is one mountain range that stretches from Georgia to Maine. And the idea that it belongs only to the southern part of the mountain range defies logic to me,” O’Neill said.
What Do You Think?
How about you? Do you call yourself an Appalachian? Why or why not? Send us an email to InsideAppalachia@wvpublic.org.
------
Our theme music is by Matt Jackfert. Other music this week was provided by John Wyatt, John R Miller, Alan Cathead Johnston, and Dinosaur Burps. Roxy Todd originally produced this episode. Bill Lynch is our current producer. Our executive producer is Eric Douglas. Alex Runyon was our associate producer on this original episode. Kelley Libby is our editor. Our audio mixer is Patrick Stephens. Zander Aloi also helped produce this episode.
You can find us on Instagram, Threads and Twitter @InAppalachia. Or here on Facebook.
Inside Appalachia is a production of West Virginia Public Broadcasting.

107 odcinków
Wszystkie odcinki
×Zapraszamy w Player FM
Odtwarzacz FM skanuje sieć w poszukiwaniu wysokiej jakości podcastów, abyś mógł się nią cieszyć już teraz. To najlepsza aplikacja do podcastów, działająca na Androidzie, iPhonie i Internecie. Zarejestruj się, aby zsynchronizować subskrypcje na różnych urządzeniach.




