Przejdź do trybu offline z Player FM !
Robot Gaze Aversion
Manage episode 229666399 series 86854
BOB HIRSHON (host):
Refining robot social skills. I’m Bob Hirshon and this is Science Update.
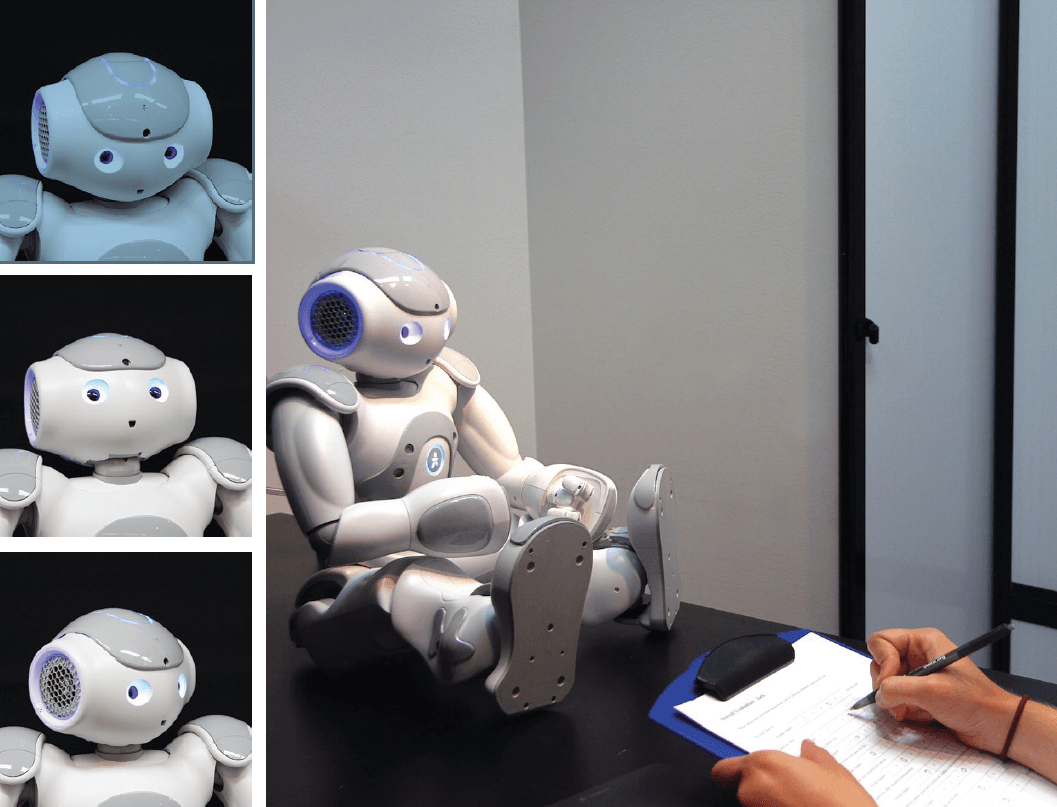
Making eye contact is an important social skill, but so is occasionally breaking eye contact. That’s true for robots as well. Bilge Mutlu is a professor of computer science, psychology, and engineering at the University of Wisconsin, Madison. His team found that humans were most comfortable talking to robots that glanced away in typical human patterns: to signal the other person’s turn to speak, for example.
BILGE MUTLU (University of Wisconsin, Madison):
People don’t interrupt the robot when it’s averting its gaze. And both when no aversion, or, sort of badly timed aversions happen, people are more likely to interrupt the robot, they think the robot’s not as thoughtful, and they don’t think that the robot’s behaviors are intentional.
HIRSHON:
Next, Mutlu says he’d like to teach robots more sophisticated gaze aversion habits: for example, making them respond to changes in eye contact from their human partners. I’m Bob Hirshon for AAAS, the Science Society.
——————————
This research was a project of the Human-Computer Interaction Laboratory at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, co-led by Professors Bilge Mutlu and Michael Gleicher, and carried out by graduate student Sean Andrist and undergraduate student Zhi Tan.
The post Robot Gaze Aversion appeared first on Science Update.
34 odcinków
Manage episode 229666399 series 86854

BOB HIRSHON (host):
Refining robot social skills. I’m Bob Hirshon and this is Science Update.
Making eye contact is an important social skill, but so is occasionally breaking eye contact. That’s true for robots as well. Bilge Mutlu is a professor of computer science, psychology, and engineering at the University of Wisconsin, Madison. His team found that humans were most comfortable talking to robots that glanced away in typical human patterns: to signal the other person’s turn to speak, for example.
BILGE MUTLU (University of Wisconsin, Madison):
People don’t interrupt the robot when it’s averting its gaze. And both when no aversion, or, sort of badly timed aversions happen, people are more likely to interrupt the robot, they think the robot’s not as thoughtful, and they don’t think that the robot’s behaviors are intentional.
HIRSHON:
Next, Mutlu says he’d like to teach robots more sophisticated gaze aversion habits: for example, making them respond to changes in eye contact from their human partners. I’m Bob Hirshon for AAAS, the Science Society.
——————————
This research was a project of the Human-Computer Interaction Laboratory at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, co-led by Professors Bilge Mutlu and Michael Gleicher, and carried out by graduate student Sean Andrist and undergraduate student Zhi Tan.
The post Robot Gaze Aversion appeared first on Science Update.
34 odcinków
All episodes
×Zapraszamy w Player FM
Odtwarzacz FM skanuje sieć w poszukiwaniu wysokiej jakości podcastów, abyś mógł się nią cieszyć już teraz. To najlepsza aplikacja do podcastów, działająca na Androidzie, iPhonie i Internecie. Zarejestruj się, aby zsynchronizować subskrypcje na różnych urządzeniach.




